Encapsulation
The packaging of electronic components refers to how the parts are installed on the circuit board. Many parts are welded to printed circuit boards (PCB) through holes, or by surface mount technology.

The simplest components are discrete passive components. These parts have only a single function, such as providing resistance, capacitance, inductance, or adding voltage or current control. Most discrete components have only two or three pins.
Resistance
The purpose of resistance is to impede the current in a circuit. The unit of resistance is ohm, represented by Ω. The resistance is encapsulated through the through-hole or SMT method. Resistance has no polarity, so it can be installed in any direction with wholesale resistors

Potentiometer
A potentiometer is a variable resistor with three terminals. The potentiometer is a resistor with a third pin that allows resistance variations between terminal 1 and terminal 2 or terminal 2 and terminal 3. Potentiometer can be used to allow the user to input a circuit, such as a volume knob.The potentiometer has no polarity. It is packaged through the through-hole and SMT method and is usually installed with wire lugs.

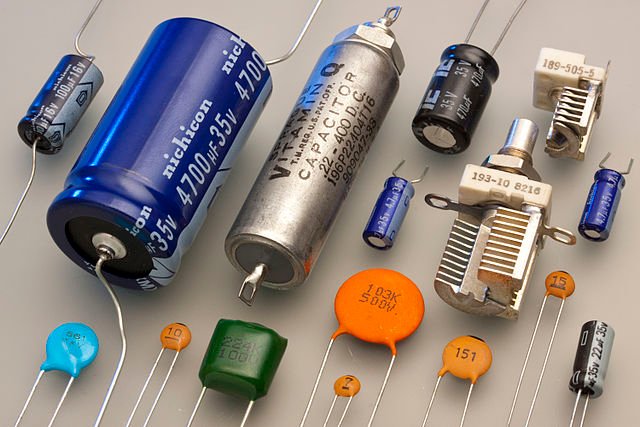
Capacitor
Capacitors store charge. Capacitors are often used for frequency filtering. The unit is Faraday, represented by F. It is also packaged by through-hole or SMT method. The electrolytic capacitor has polarity and must be installed correctly, otherwise the capacitor might be damaged. When purchasing capacitors, you must make it clear the polarity, dielectric type (e.g. ceramic, plastic, paper, etc.), rated voltage and capacitance.

Inductor
Inductors store electrical energy in magnetic fields. Similar to capacitors, inductors are mainly used for frequency filtering. The unit of inductance is Henry. Most of them adopt the through-hole or SMT package without the limitation of polarity.
Ferrite beads
Ferrite beads, also known as choke coils, provide impedance for circuit. Ferrite beads are mainly used to prevent high-frequency noise from propagating on them and are often placed at the end of the line with the connecting device.

Transformer
A transformer is basically two inductors encapsulated together that transmit alternating current from one circuit to the other via electromagnetic induction. Transformers are usually used to convert AC voltage. The number of windings per inductor determines how the voltage will be converted.

Diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate.
A diode allows or blocks the passage of current in a circuit depending on the voltage at either end. The current passes only when the voltage at anode is higher than that of cathode, usually at least 0.7 volts higher. A diode acts as a one-way valve, preventing the voltage from going in the wrong direction.
Diodes are used to convert current from AC to DC and prevent out-of-range input voltages.

Light-emitting diode
Light-emitting diodes (LED) are similar to ordinary diodes, but are mainly used to emit light.

Photodiode
Photodiodes, as opposed to LED, generate electric currents when there is light. The device is used to detect the presence of light.

Transistor
Transistors are multifunctional circuit components. This three-pin device can be used as a voltage-dependent or current-dependent switch, or as an amplifier or stabilizer depending on the circuit. There are two main techniques, bipolar junction (BJT) and field effect (FET). The pin terminals of these two transistors are different. BJT transistors are further divided into two types, NPN and PNP, according to the polarity of the components. FET transistors have many classifications according to N and P channels.